Monitoring Torrents On Your Server
There are a lot of clients to manage torrents on your server: deluge, rtorrent, … but I decided to settle with transmission, mainly because it’s already installed in most of the distributions I had to manage and it provides a really handy daemon to manage all your downloads.
Setting up
In case transmission is not already installed, you’ll have to do it, on Debian and Fedora the packages of interest are: transmission-{remote,common,daemon}. Additionnaly, you’ll also need tmux (I’ll come back on this later). You may want to run the daemon as your user, if for one reason or another you don’t, you’ll have to manually kill the transmission process and restart it after each reboot.
sudo kill $(pgrep transmission) && transmission-daemon
or better versions suggested in the comments on Lobsters:
sudo pkill transmission && transmission-daemon
To give it a chance to quit gracefully:
sudo pkill -INT transmission && transmission-daemon
Downloading torrents
The CLI is pretty straightforward, when I mention CLI, I talk about transmission-remote, not transmission-cli. beware of using transmission-cli though, it has been deprecated in favor of transmission-remote, and it’s less handy because it runs as a foreground process, so when you launch your torrents with transmission-cli, unless you add the ampersand (&) it will lock the current terminal (which is far from ideal if you’re using ssh), plus you have no way of getting the state of all your downloads at once. The simple and modern command to add a new torrent is:
transmission-remote -a /path/to/torrent/file
Or if you have a magnet link:
transmission-remote "<magnetlink>"
Note the quotes when you want to add a magnet link, although not necessary all the time, I found some magnet links that simply didn’t work without, so it’s a good practice. After that, you can verify everything is good with:
transmission-remote -l
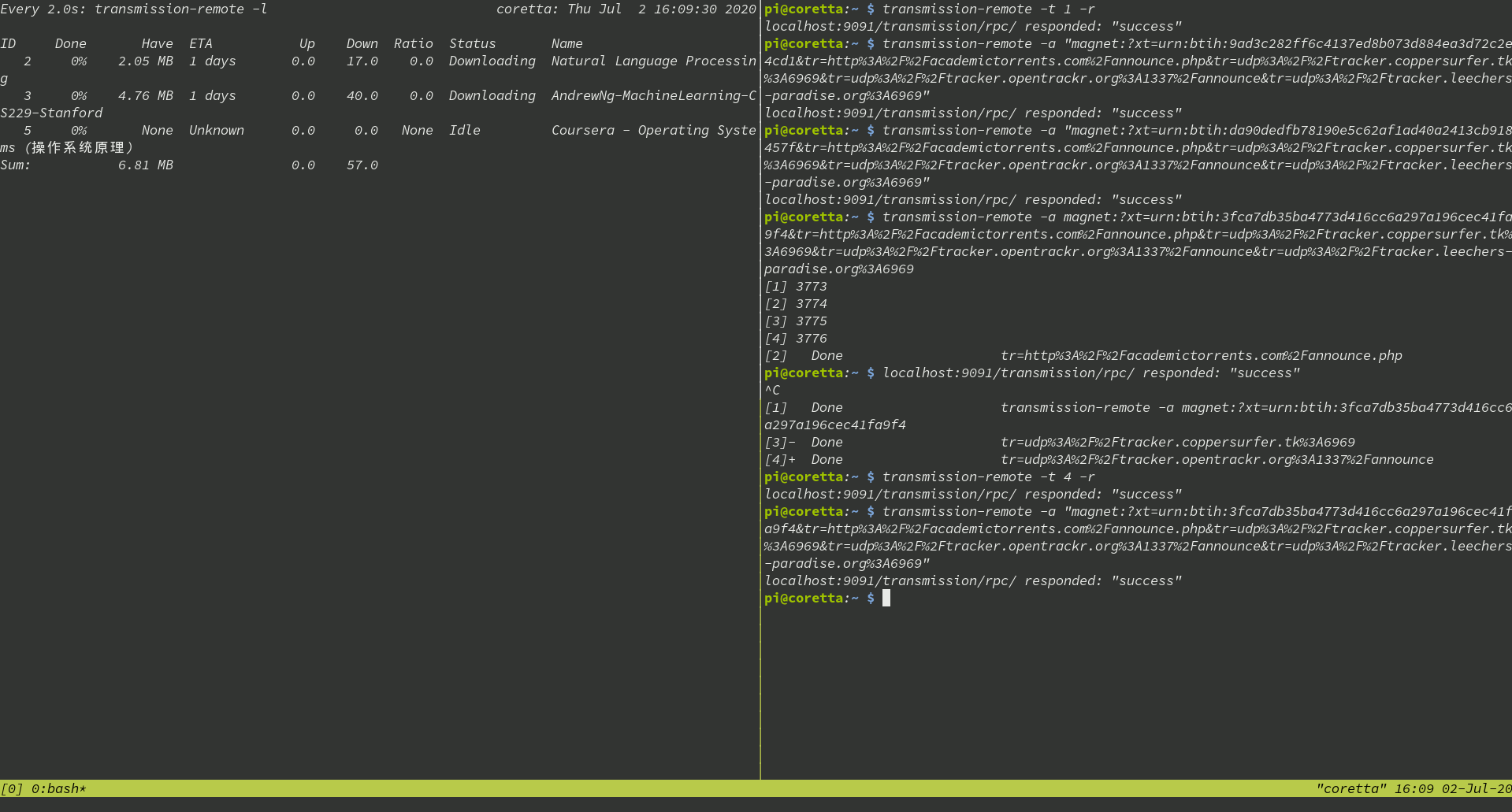
Keep track of what’s happening
This is where tmux will be helpful, if you don’t know what is tmux, here is a quick introduction, for now you just have to launch tmux, then run the command:
watch "transmission-remote -l" (add the -n flag to specify an interval, the standard is 2 seconds)
Then Ctrl-B + % to divide the screen and you can now operate on transmission as you wish, and you’ll no longer have observability problems
Rounding edges
You might experiment connection slow down when torrenting, it’s because the torrent protocol is extremely efficient at maxing out your connection, so it uses all available resources to get the job done quicker. To “fix” that, you can limit download and upload speeds in ~/.config/transmission/settings.json